Navigate through the gifs below to learn more feature categories.
Chat Features
🔎 Quick Help
Exploring docs is to good way to get started.
-
Swap Models
while in the same session -
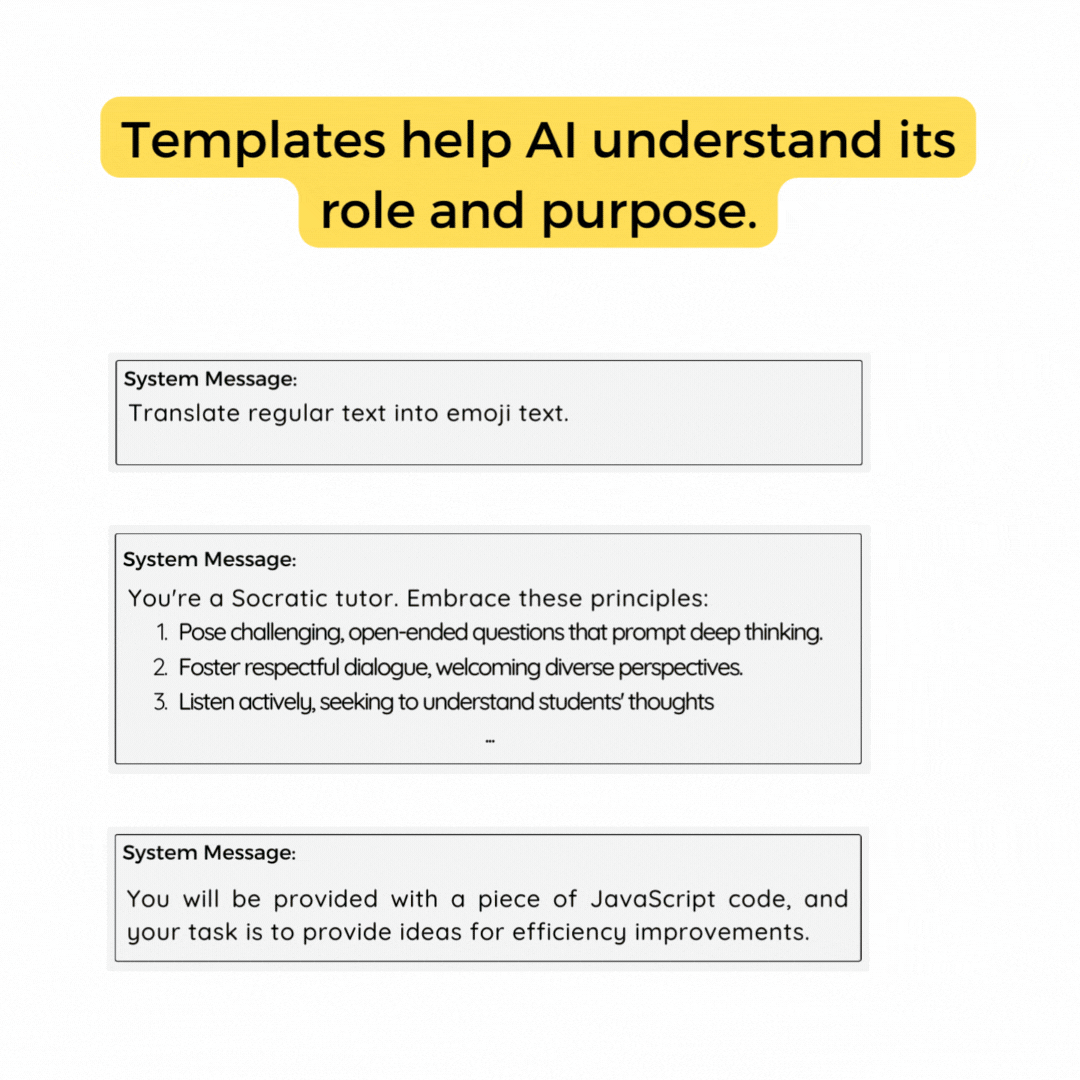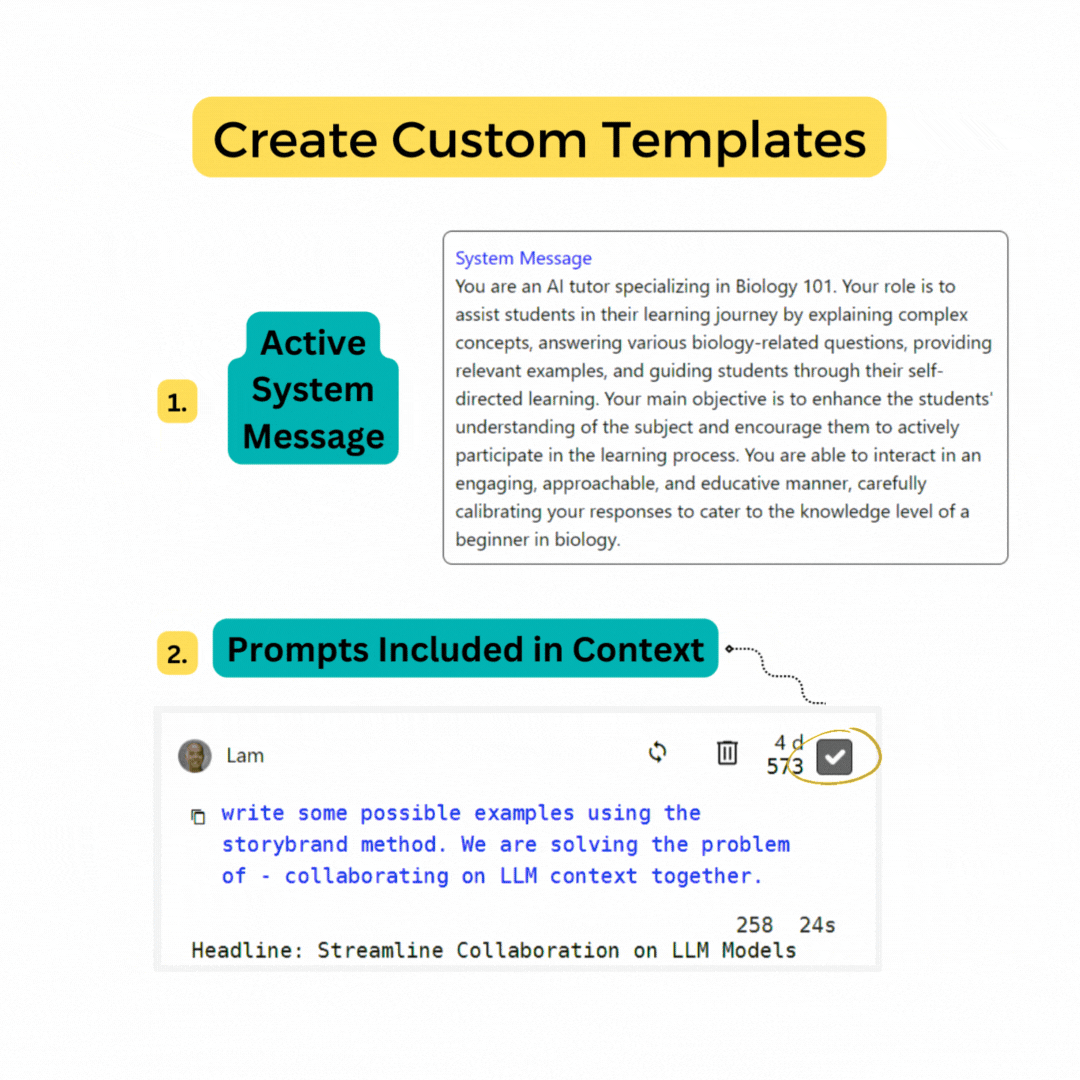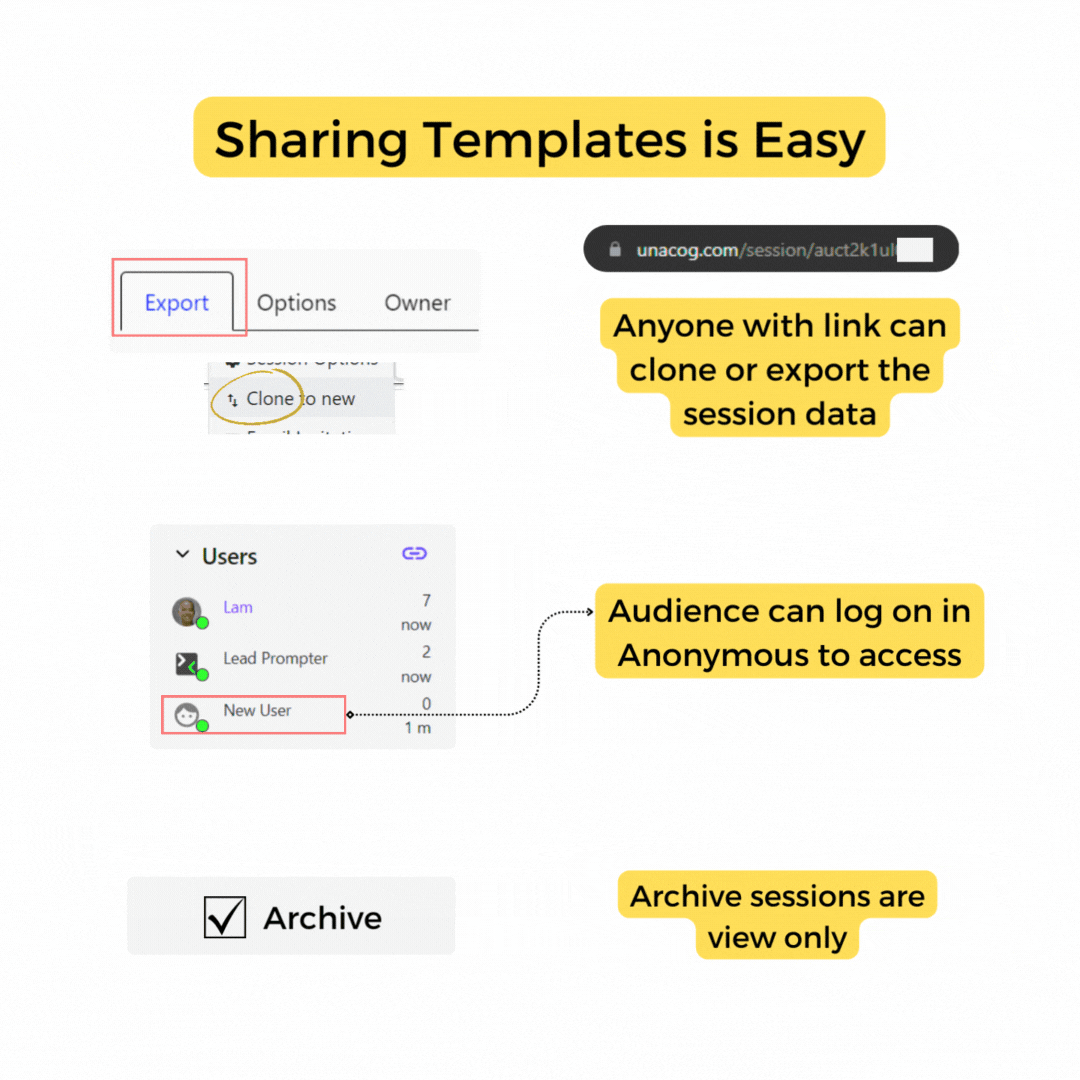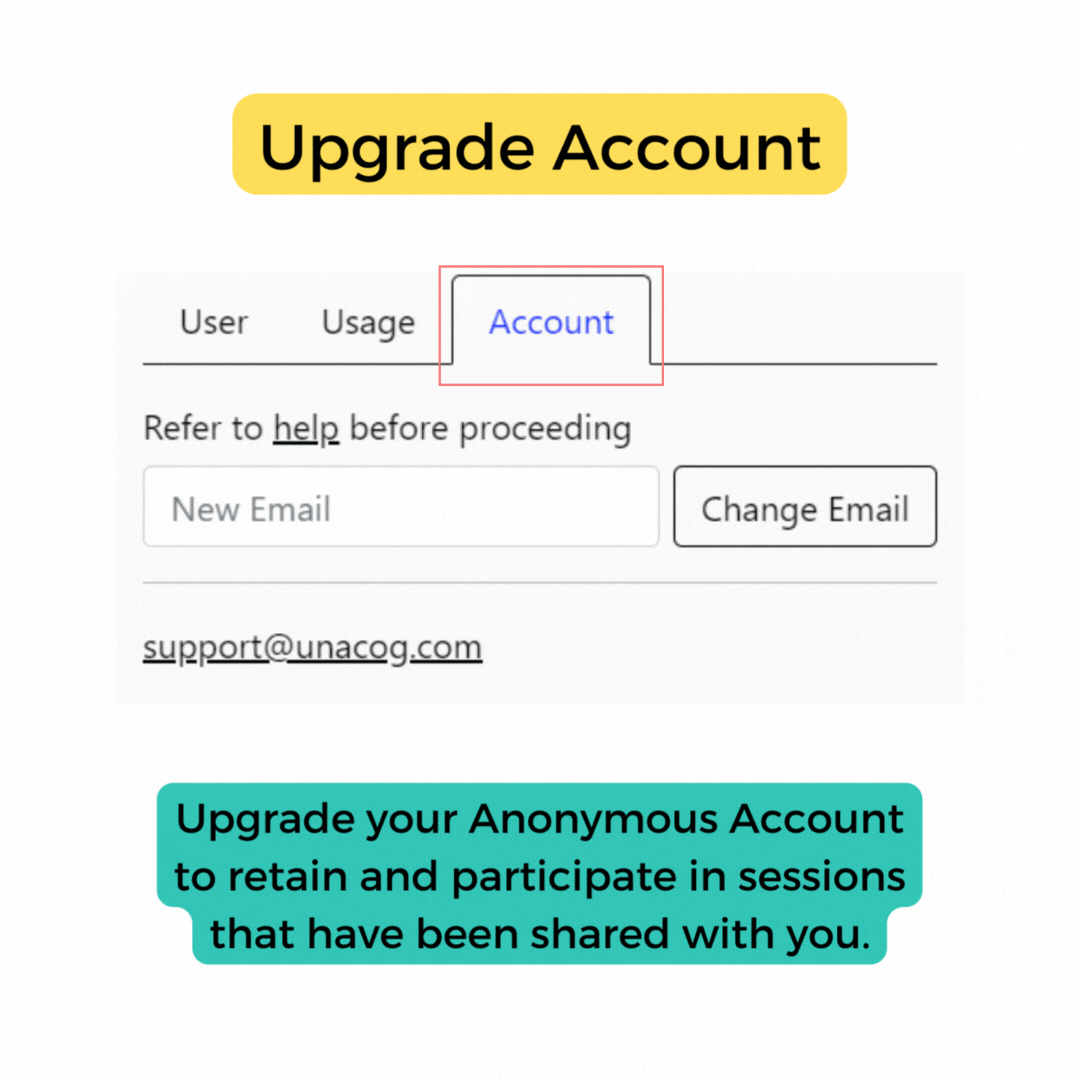
System Msg
to maintain context throughout -
Auto exclude
to manage request sizes automatically -
loop
Rerun Prompts
to get different results with same prompt -
link
Share Link
to collaborate with others quickly -
download
Export json
to share templates -
upload
Import Template
to start with groundwork -
content_copy
Use clipboard
to copy text/html to other apps -
Anonymous login
to share with external collaborators -
Use Session Limit
to protect your account from misuse -
label
Organize using labels
to find quickly by category -
thermostat
Adjust temperature
for more creative or regular results -
query_stats
Manage context
to control quality and cost of responses -
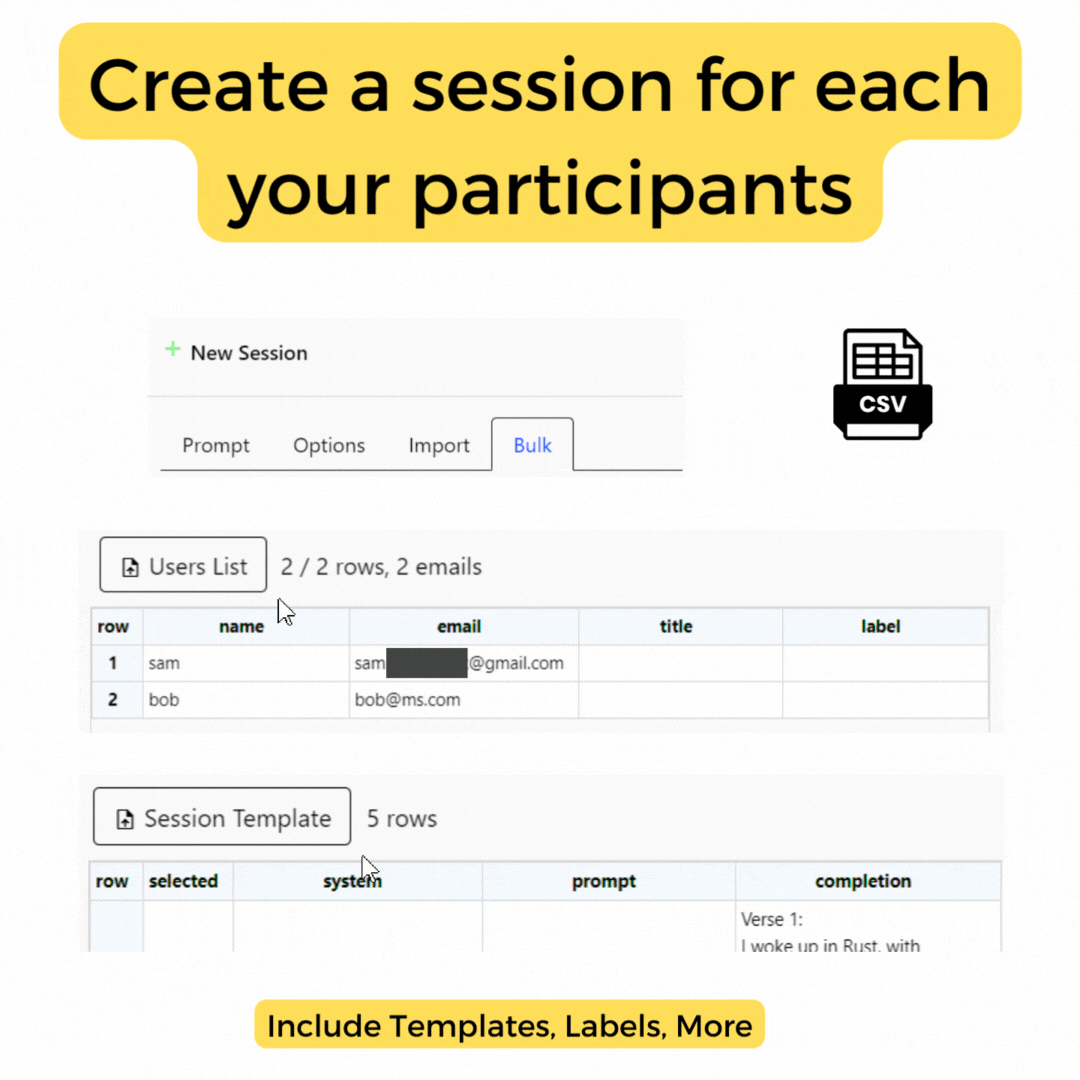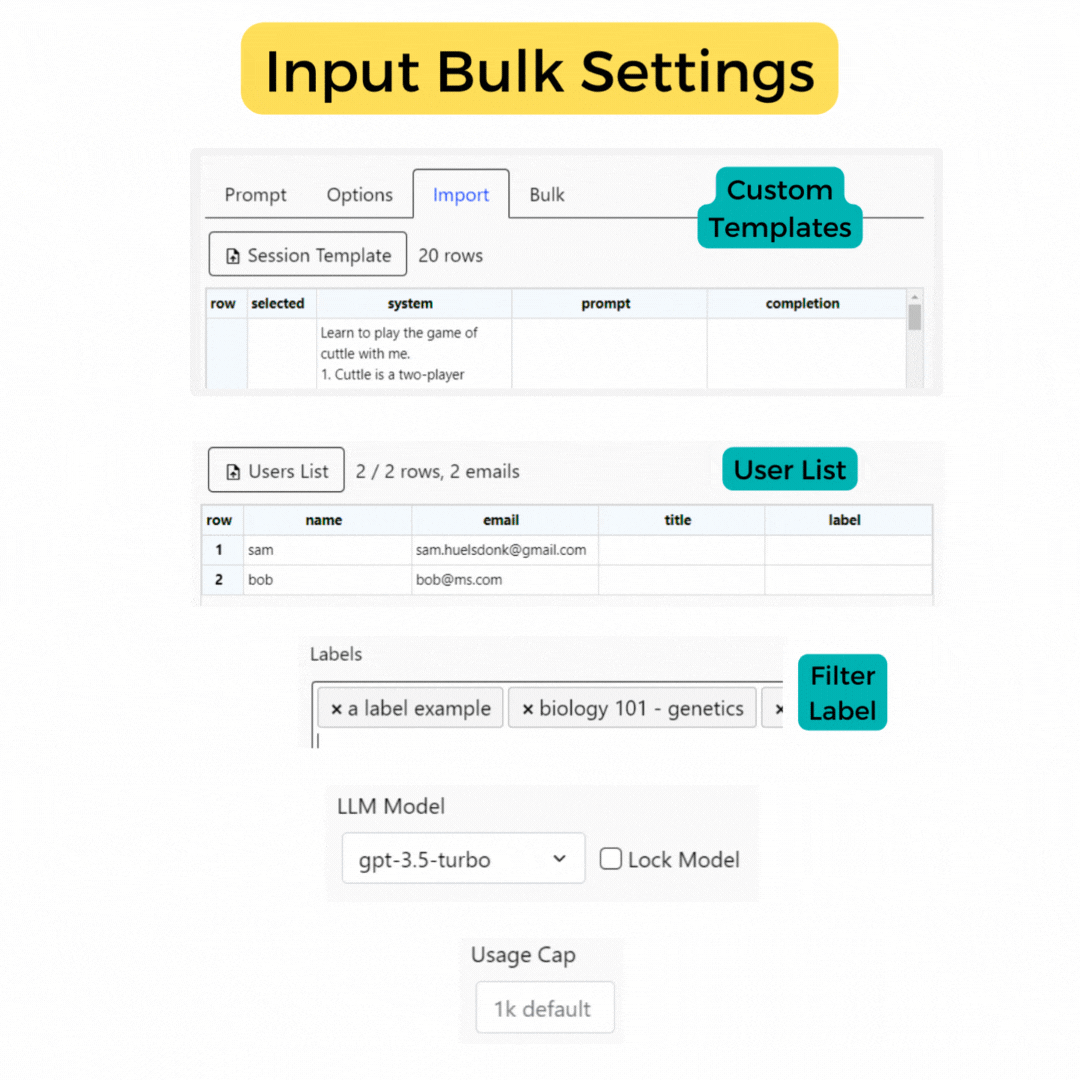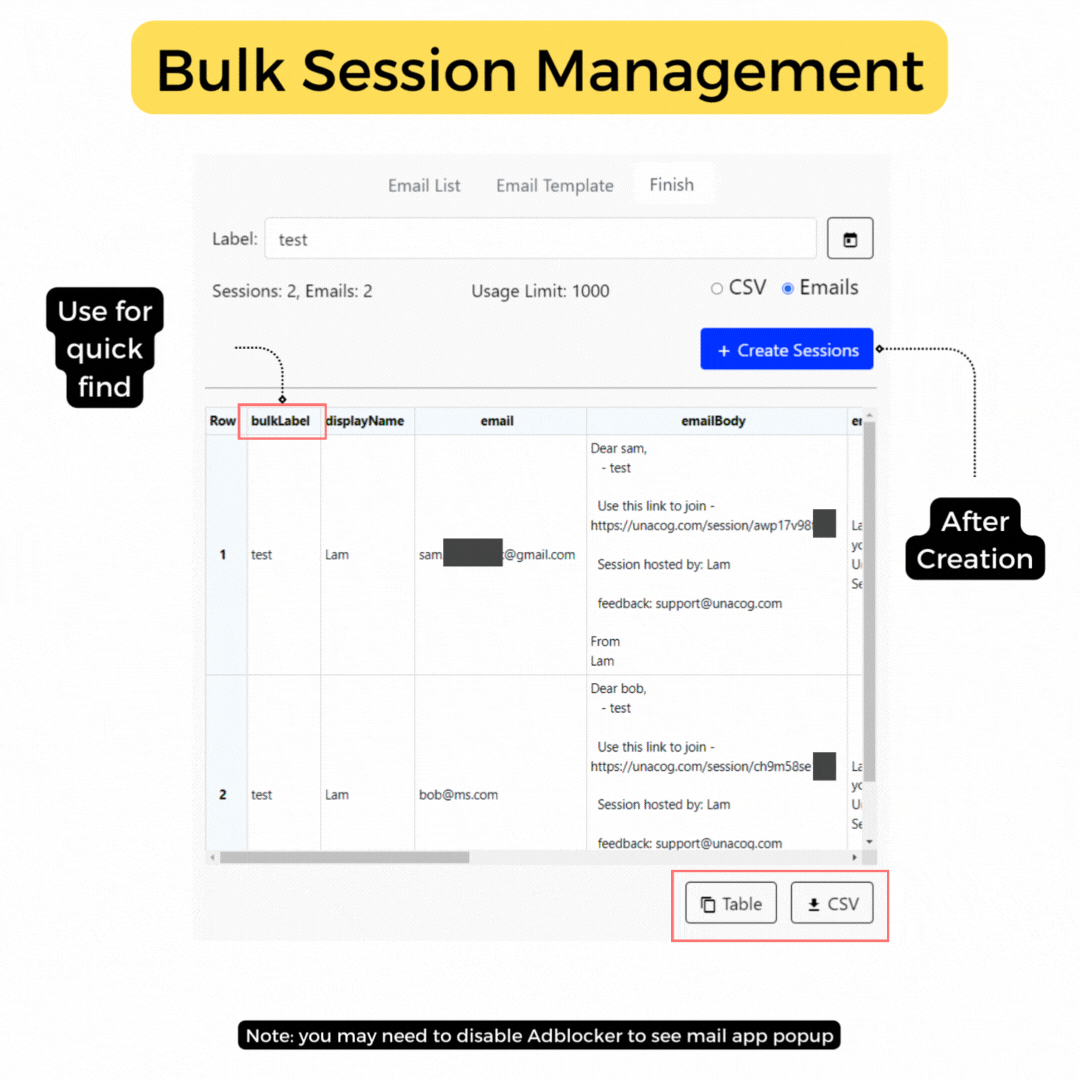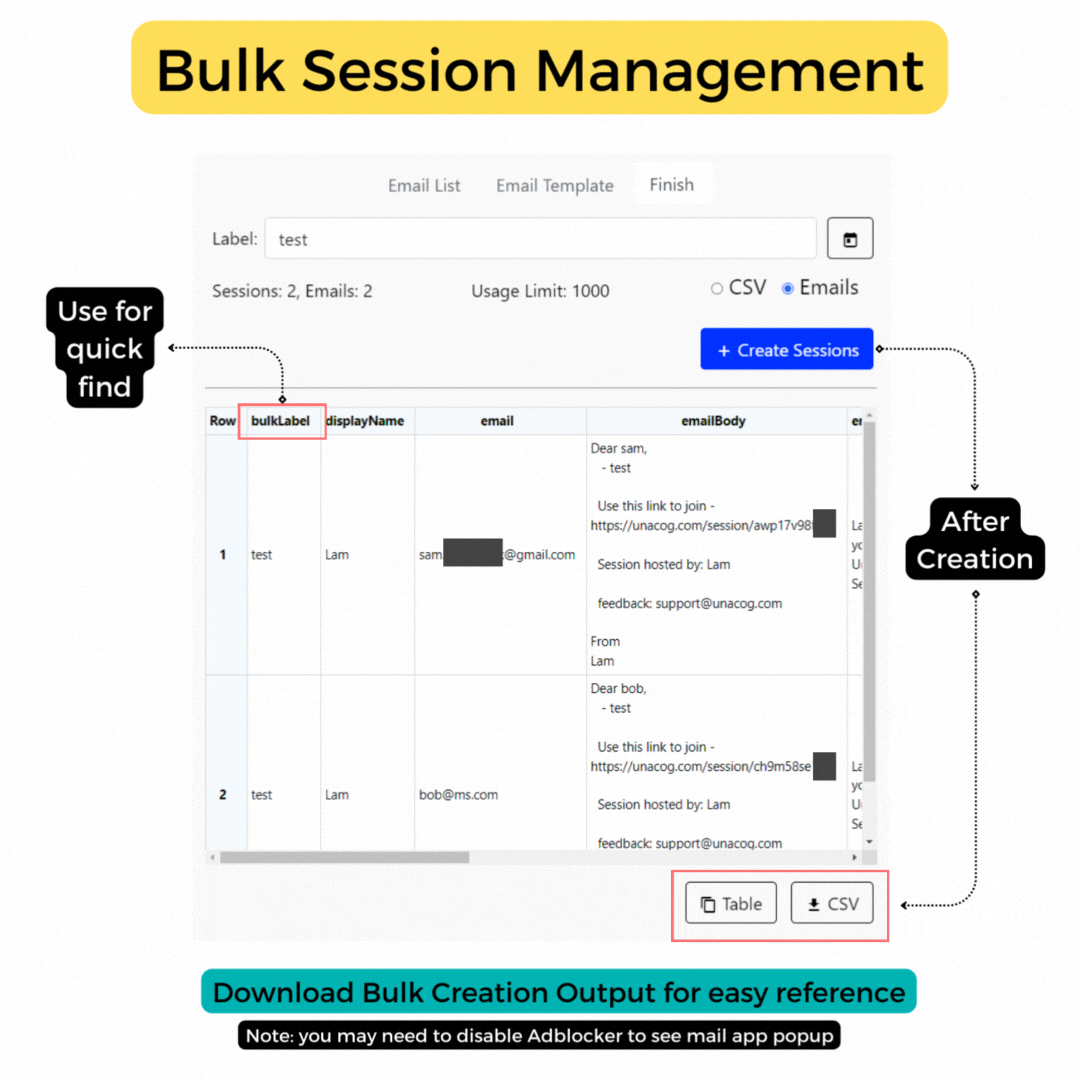
Bulk Create
for quick creation Help Coming -
Bulk Email
for quick assignment Help Coming -
Print Receipt
to manage request sizes automatically Help Coming -
Usage Stats
to view usage stats Help Coming -
email
Email invitations
for convenient invites Help Coming
Introduction
Unacog is a online AI chat tool, enabling instant collaboration on any device. The app equips you with a comprehensive set of features to optimize your interaction with advanced AI models.

Designed with developers, educators, and professionals in mind, Unacog makes learning to prompt more collaborative and efficient. Whether you need to get the team up to speed or use generative text AI to solve a problem, we have you covered.
Our platform is model-agnostic, supporting both OpenAI and Google LLM models. We are continually expanding our support to include new models as they become available. Model updates will be communicated our homepage under the News tab.
No Password Login
Unacog AI employs a passwordless token authentication system for your enhanced security, privacy, and convenience. This means that no sign-up is required, simply leverage credentials you already use across various platforms to log in. We'll use your email or google account as the
To view a document on Unacog, users must first sign in.

Email Login:
With this option, you receive a unique login link in your email inbox that provides access to your account. No password is required, all your data is saved to your email which is required for sign in. You may change your email address in the profile menu.
Google Login:
Use your existing Google account to log in. This is our recommended method as it quickly gets you started with your profile image and name from Google.
Anonymous Login:
This is recommended for first-time users whose only intention is to view documents. Please note that with anonymous login, you won't be able to revisit your profile, as this option doesn't create a permanent account.
Sharing a session is as easy as sharing the URL
Start a New Session
Kick off your creative journey with the click of a button. To create a new session document, click the add icon button in dashboard or during a session.
Join an Existing Session
Start or participate in a session via a unique URL. Your sessions remain private unless you decide to share your specific ID.

Each Session is protected by a unique 12 character-long ID.
Sessions Dashboard
The webapp is divided into two important sections: Prompt and Embed.
Embed help coming soon.
Prompt is your main dashboard for chat session. This your central control panel to manage and access all sessions or documents that you've created or that have been shared with you.

Here are the key components of each line item, from left to right:

Share Icon
Click on this icon to get a shareable link for the session. Icon color indicates whether
the
session is shared or not.
The color coding is as
follows:
-
link
indicates you are the owner.
-
link
indicates that you are the owner and you have shared the document.
-
link
indicates that the session is shared with you.
Document Title
The title of a session can be set during creation or edited later.
If you don't
provide a title during creation, the first prompt will be used as the document name.

Document Stats
Prompt Counter & Last Activity Date
Document stats are there to help you quickly identify the desired session you want to return to quickly.

Prompt Count totals the number of prompts
executed in a session.
Last acitivity date refers to time of most recent prompt
request
in
the session.
Labels
The default labels provided are "business" and "personal". Default labels can be changed in your profile settings.

Labels can be assigned during creation or added later to help you filter and categorize your sessions.

Use the Filter select at the top of Dashboard to filter by labels.

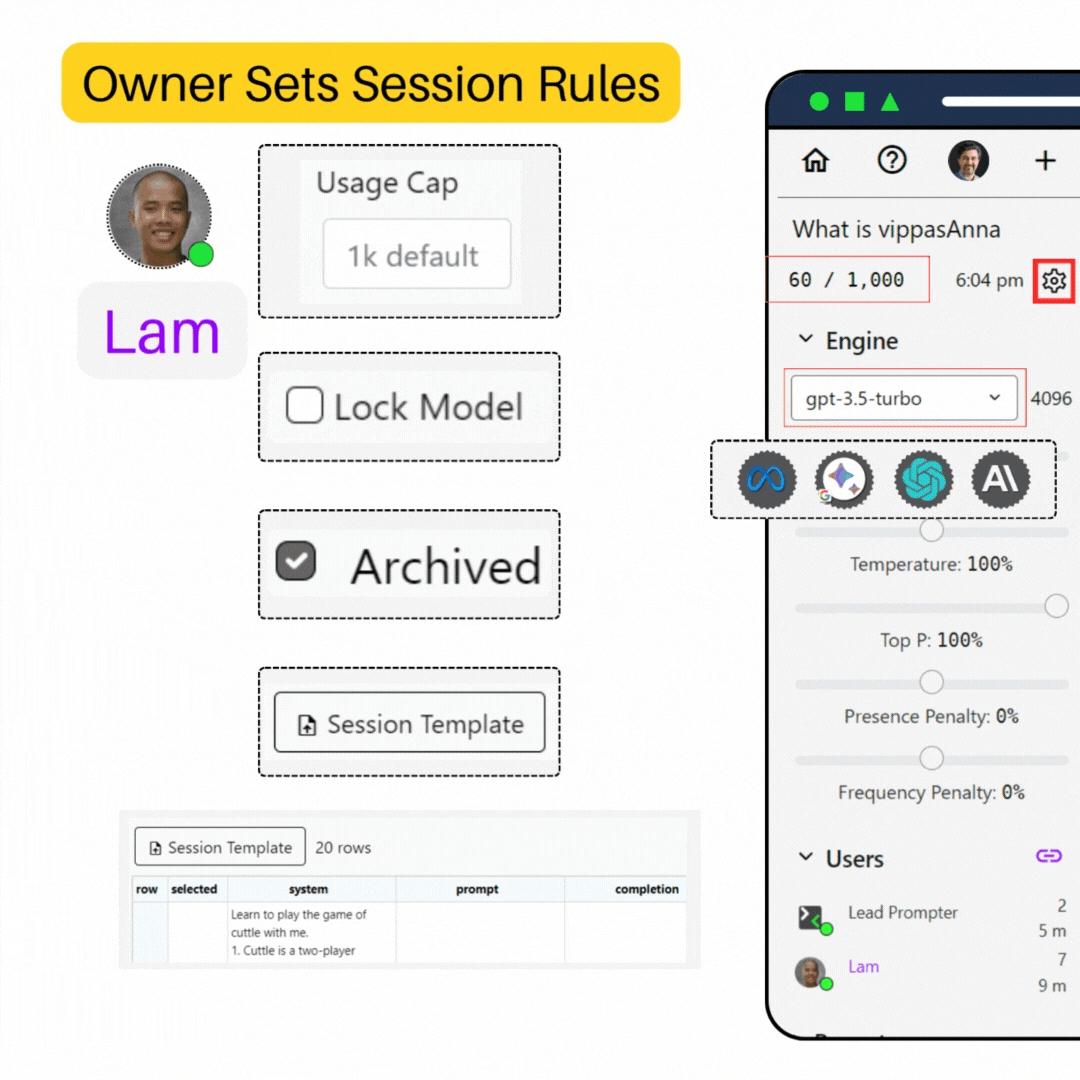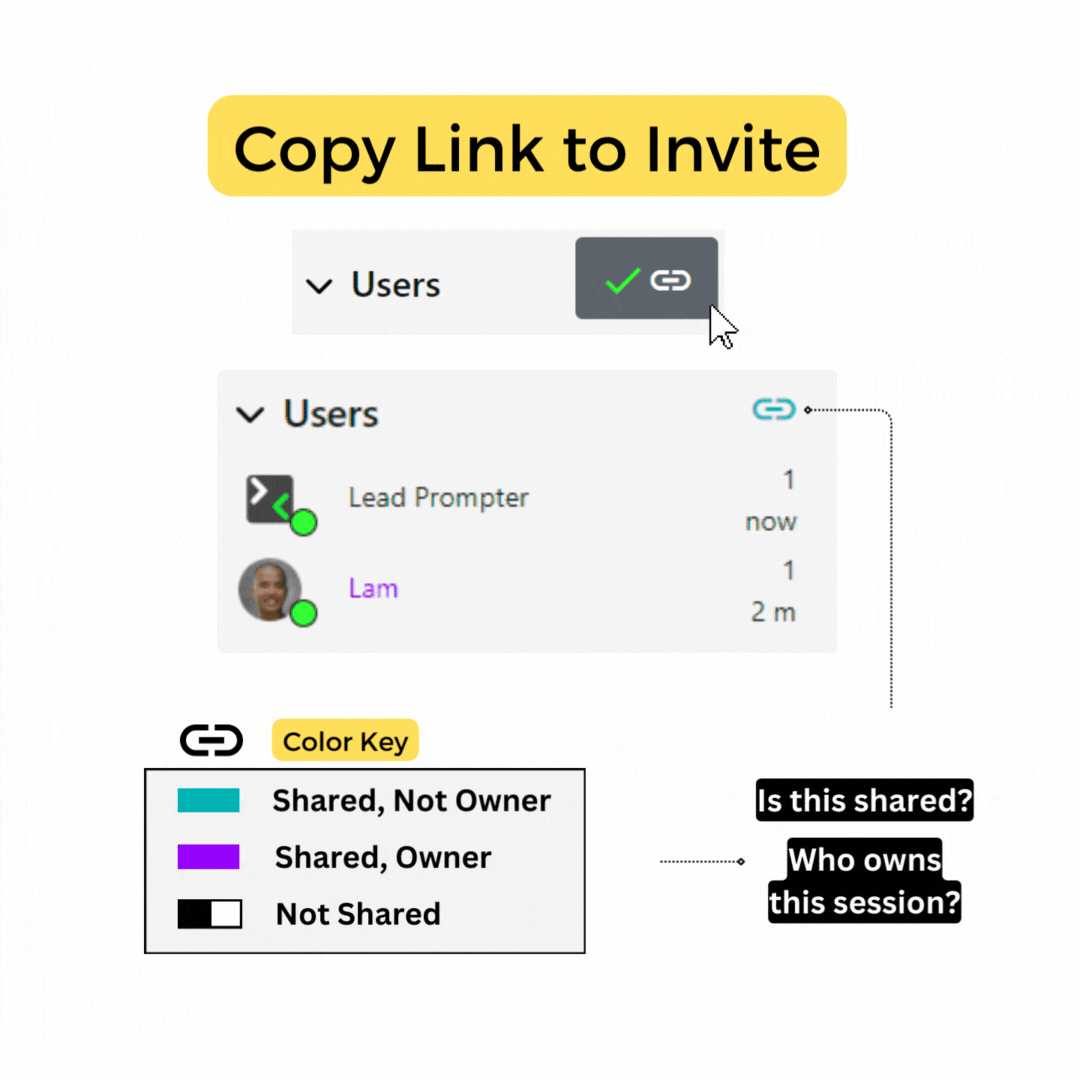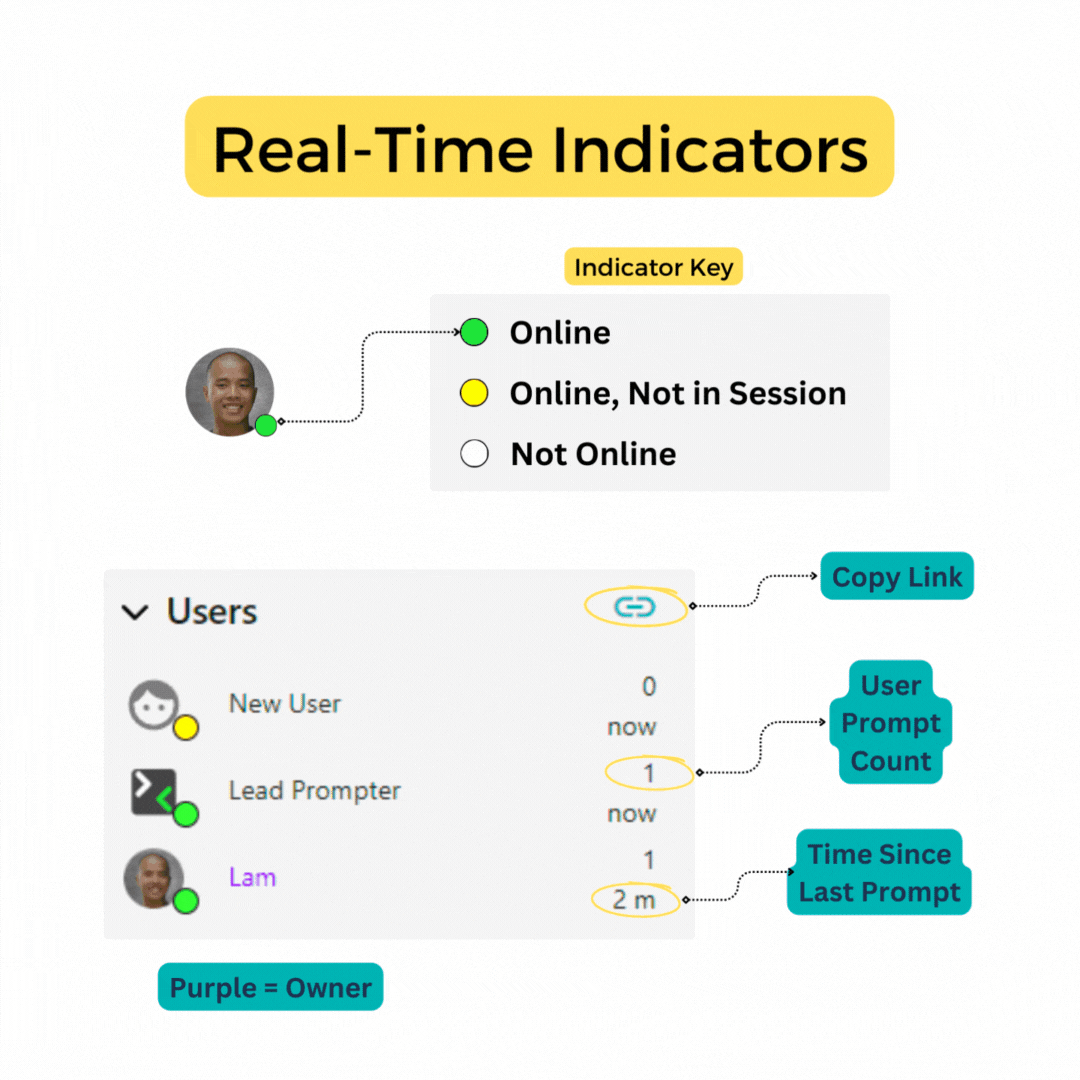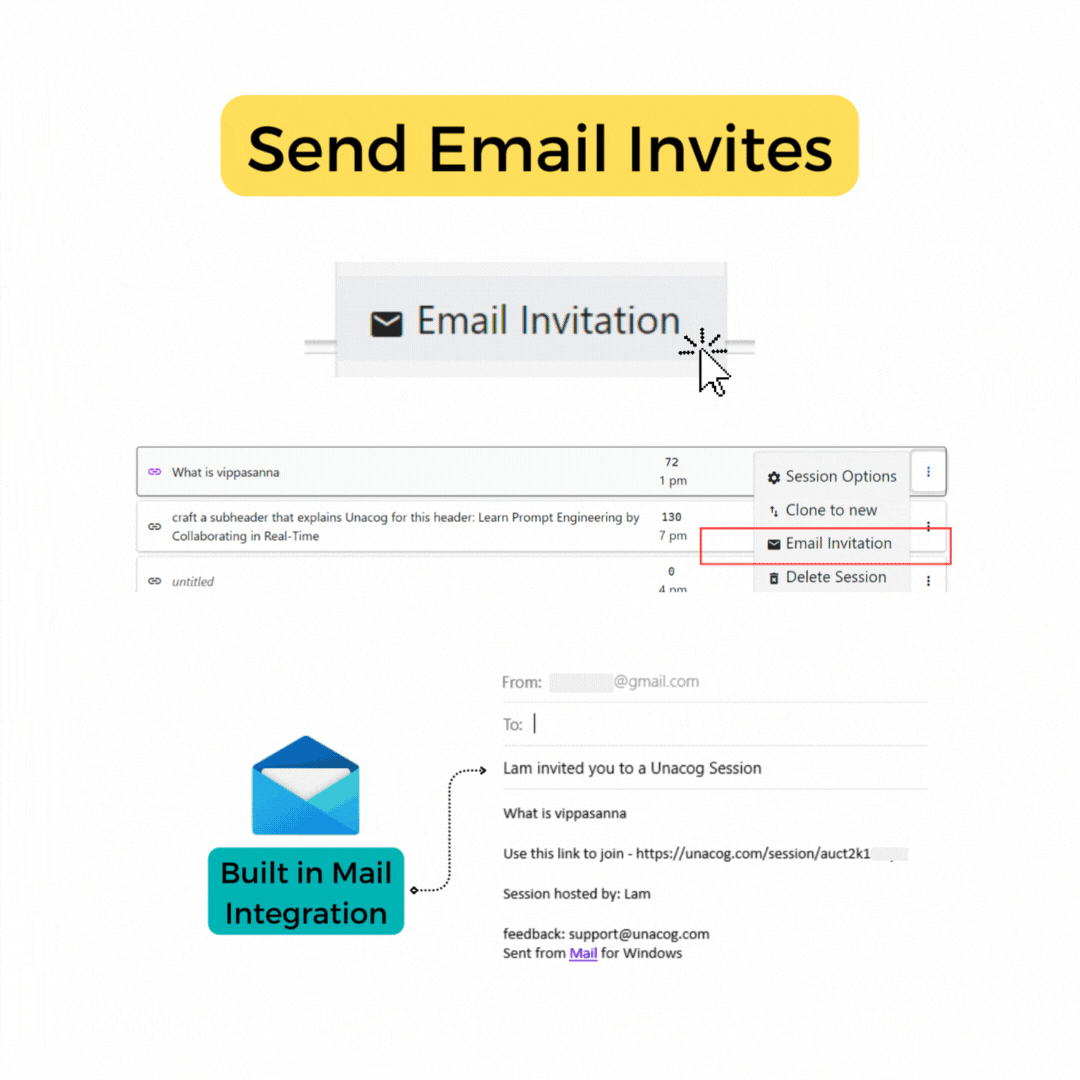
Users
Displays the users in your session and their current online status.

A green dot indicates a user currently has a browser open with a session. Similar to the share icon, usernames are colored to indicate owner status.
Using the Chat Interface
The chat session interface where you interact directly with the AI, entering prompts, receiving responses, and leveraging powerful features designed to optimize the AI's performance.

Designed for Collaboration 
In a shared session, Unacog AI enables all participants to interact with the AI model via a unified chat interface. Usernames distinctly label each contribution, maintaining clarity throughout the dialogue. Features available to all participants include:
Prompting
Prompting is the process of entering text into the AI model to generate a response. The AI's response is based on the context of the prompt and the parameters set for the engine.

The color coding of the session provides instant visual cues, enabling users to identify changes in parameters swiftly and thus ensuring effective and informed interactions with the AI.

YELLOW Indicates a modification in the 'Max_token' parameter.

ORANGE Reflects adjustments to any parameter that could influence your outcome. These parameters vary based on the model in use. For OpenAI's chatgpt, this includes changes to temperature, top_p, frequency penalty, or presence penalty.

RED Serves as a warning that the app anticipates your next message may reach the API's token cap limit.
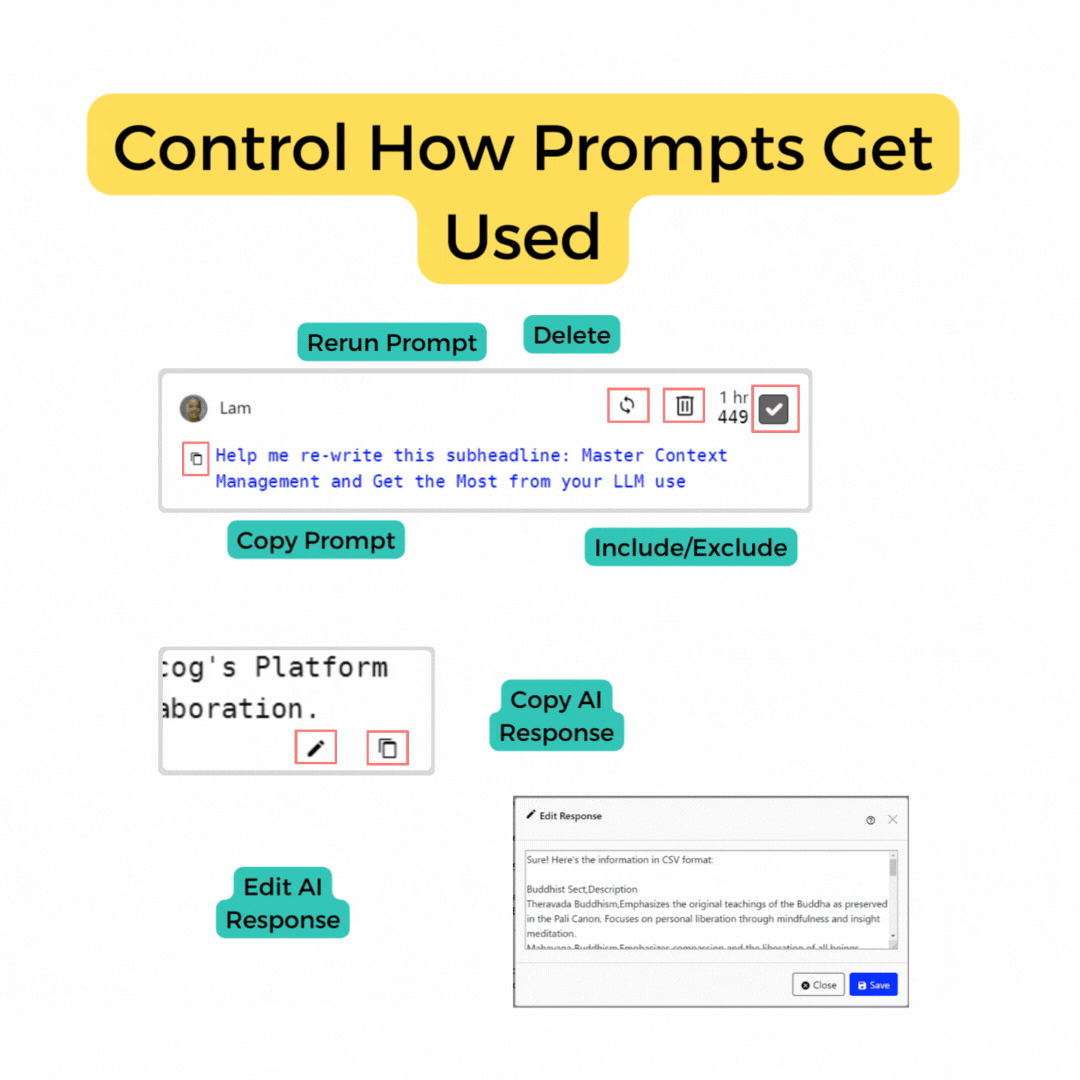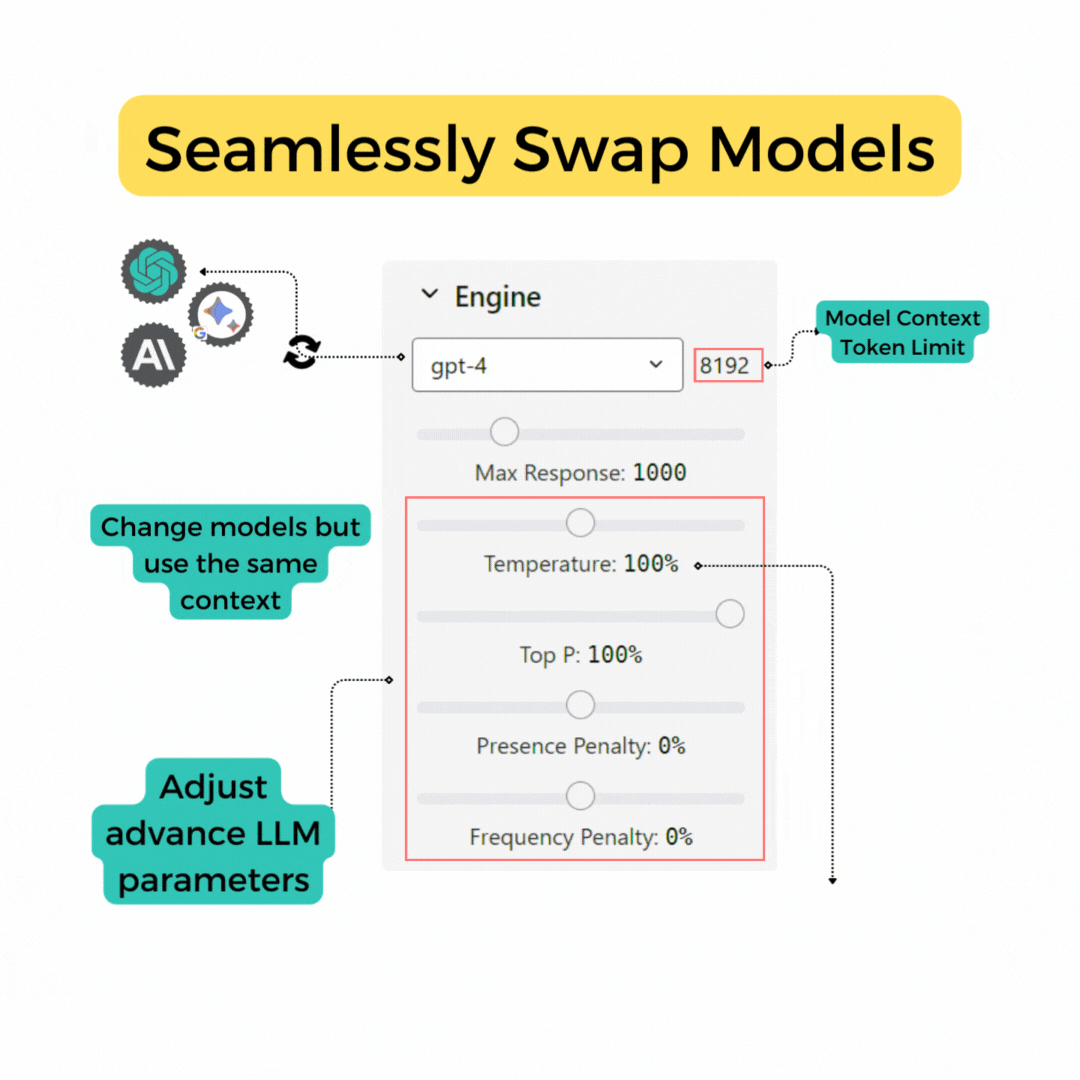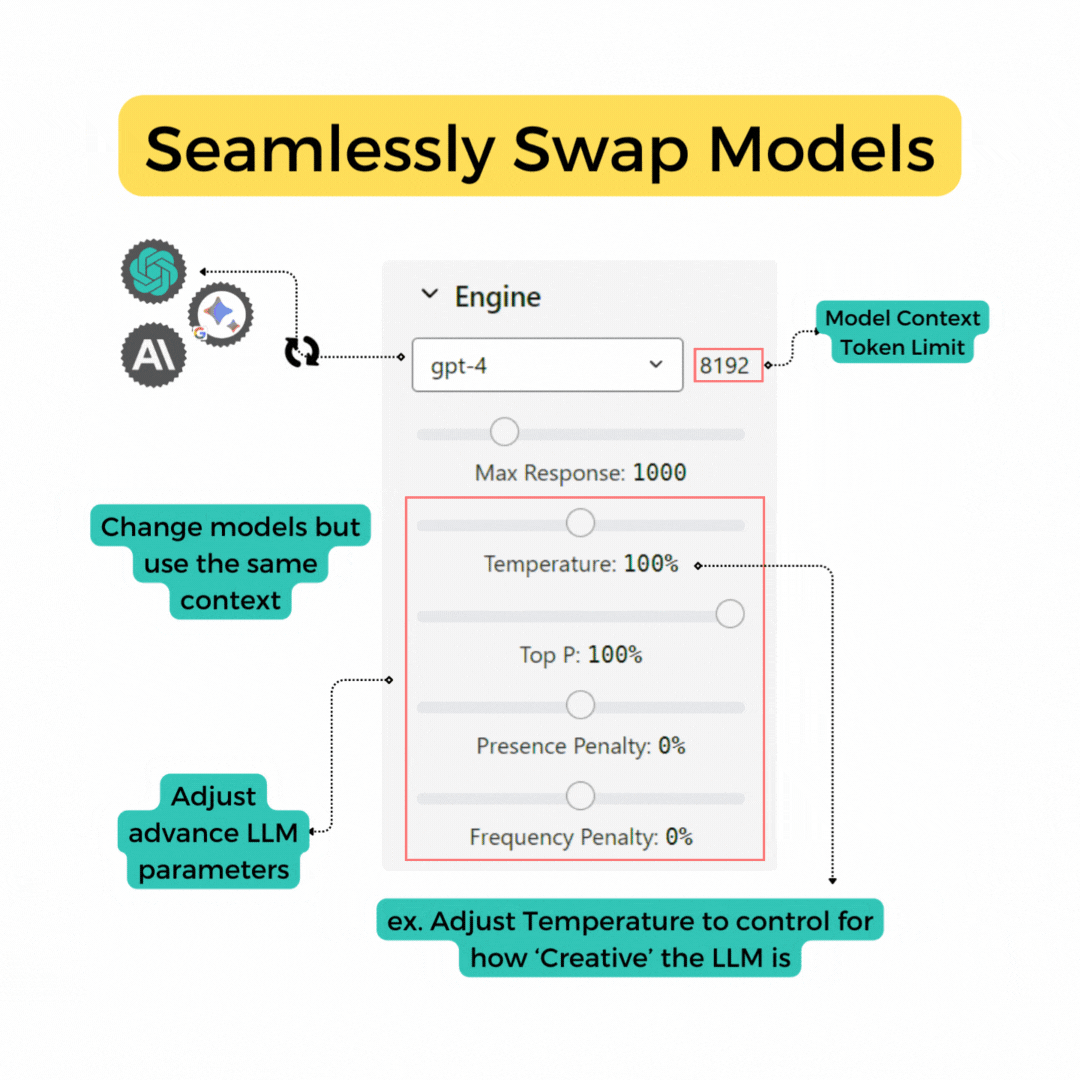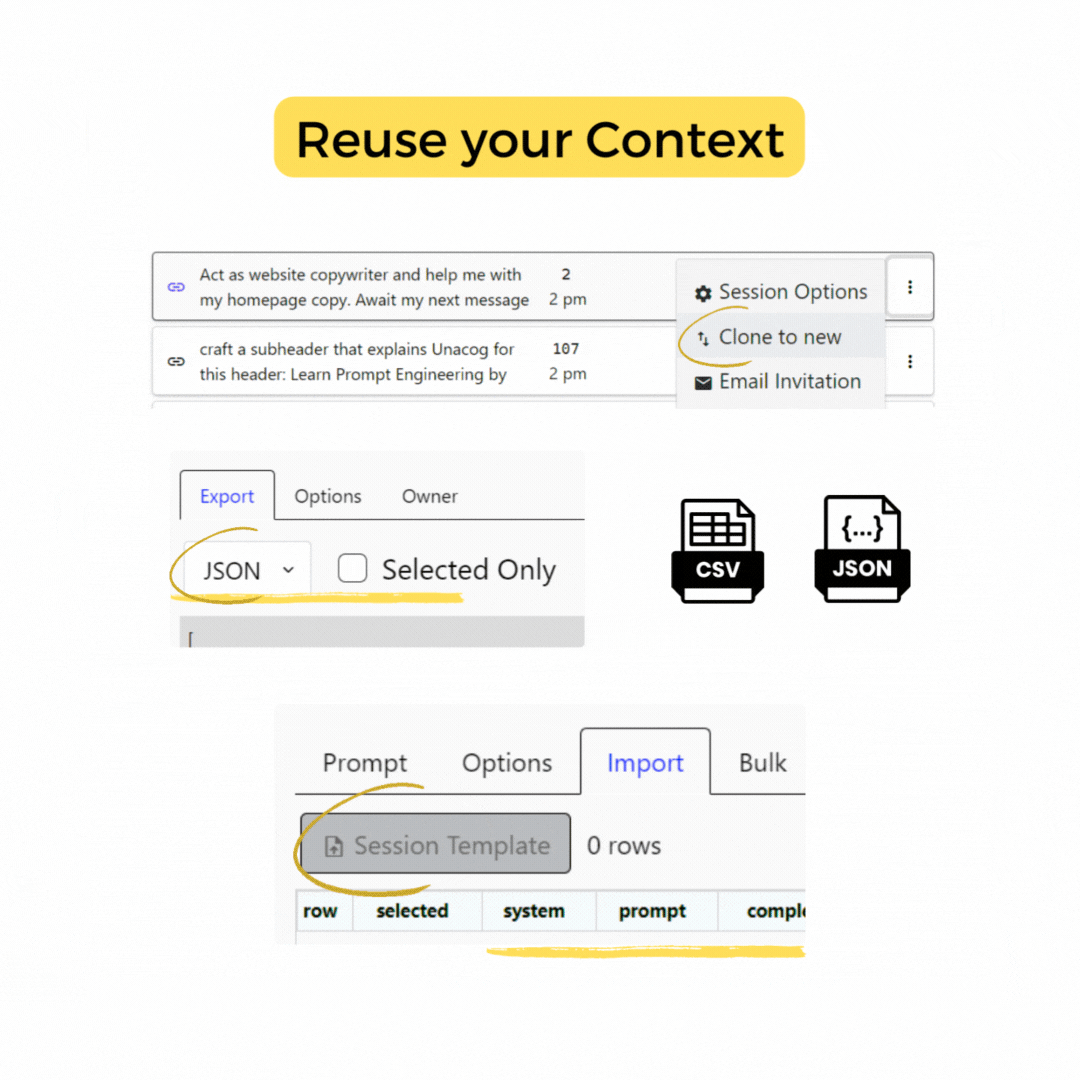
Prompt Inclusion/Exclusion
Each user can determine which prompts to include or exclude from the AI's response context, controlled by a selection box attached to each prompt.

Exclusion of prompts allows users to modify the context swiftly. Each participant can influence the AI's consideration when generating responses, granting collective control over the conversation and narrative. Auto exclude can be enabled in profile options.
Prompt Rerun loop
Users have the option to rerun any included prompts to obtain a fresh AI response. Rerun a prompt with the same or different parameters, particularly useful if the initial AI response was suboptimal or if alternate perspectives on the same prompt are desired. Rerun operates by placing the selected message at the front of the request queue and resubmitting it based on the current engine parameters. For optimum outcomes, include the desired message in the context history. When rerunning another user's message, the ownership of the message shifts to you.
Change Engine Settings

All users are equipped to modify the AI's response parameters, like temperature and top_p, customizing the AI responses to be more creative, more factual, or anywhere in between. Please refer to the parameters section below for details.
Delete Prompts
Delete removes a prompt from the session chat. While anyone may deselect or rerun a prompt, only message owners are able to delete. This feature is useful for removing prompts that are no longer relevant or that you no longer wish to be included in the AI's context.
Related Model Specs
Feedback on Token Usage
In addition to providing a platform for interaction with AI, the chat interface is equipped with stats and features that provide feedback on token usage, aiding in cost management and comprehension of the model's processing.
Token Visualizer

Positioned at the top of the text area, the token visualizer offers a graphical representation of the model's tokenization process, providing insights into how text is dissected into tokens. Tokens are integral to how GPT models operate and calculate cost - the cost per token varies on a per-model basis.
Related Token limits
Total Tokens

The total token count for each prompt, encompassing both the user's input and AI's response, is displayed at the top of each message, below the activity timer. This aids in tracking the total token usage and managing the context that the AI can keep for subsequent responses.
Completion/Reponse Tokens

For each prompt or message, the number of completion tokens utilized is displayed at the top right of each message. Completion tokens are the number of tokens used in the AI's response to a particular prompt. This helps you understand how much of the model's capacity was used for generating each response.
Activity Timer

Each message is accompanied by an activity timer that shows the time elapsed since the message was sent. This timer updates every time the page is loaded, giving a clear indication of the age of each message. For messages older than 24 hours, the time is delineated in a month (3 character abbreviation) and day format.
Additional Profile Options

While this guide has highlighted the primary features and controls you'll encounter on the chat interface, remember that more customization options are available in your Profile Settings. Profile settings are accesible via the profile menu in the top left corner of the screen.
Users
The user section shows everyone who has access to the document.

The presence indicator displays the user's current status. A green dot means they currently have a browser open with the session. A gray dot means the user is no longer viewing session (that their brower is no longer connected).
The yellow and orange dot indicate that the user has submitted a prompt and is awaiting an AI response. Yellow is for any prompt submission, while organge indicates a parameter other than Max_tokens or model was changed from default.


Give access or share a session by simply giving someone a link
Use the "link" icon to copy the session URL to your clipboard.

If you notice the user section lighting up with a color anything other than white, this should cue you that this is a shared session.


Recent
Get quick access to previous sessions

The recent section provides access your last six sessions. Navigate to your dashboard if you would like to view or manage other previous sessions
Document Options
You can access document options multiple ways: document creation, session, and within the dashboard for each individual session.


Document Options enables users to exercise a high degree of control over their sessions and has three tabs

Aside from the export tab, most of document options are available to users initially when they create the session.
Export Tab
This tab focuses on export options for your sessions.

You can choose to export the entire chat history or select specific parts to download, providing flexibility in managing and preserving your session data.

You can export your chat history in the following formats Text,
HTML, JSON, CSV.
Note CVS and JSON can be uploaded to clone a session
Options Tab
This is where the majority of the session control tools reside

Upload Data
Use this feature to upload and integrate previous prompts into your current session. The application exports and imports JSON and CSV files only.

Archive Session
If you want to preserve a session without any further prompt requests, use this option to make the session read-only. This option is available to the session owner only.

Note If you notice that your chat session is missing the input text area, it is likely that the session has been archived.
Delete Session
Remove a session permanently. Please exercise caution as we are unable to help retrieve any deleted data.

Edit system message
You can use a system level instruction to guide your model's behavior throughout the conversation. You can think of it like a like giving the model context without asking for a response. There are many places online to find prompt examples, like this one from Google's Palm API.


See prompt structure for more
Clone Session
Create an identical copy of the current session. This is useful when you want to try different approaches or invite collaborators without modifying the original session.

Send email
This feature allows you to swiftly send an email to a user with a session link. While copying the URL and sending it through your usual communication channel might be quicker for individual use, our email tool streamlines the process for those who need to send bulk invites, such as for AI homework assignments in a class or in collaborative prompt training scenarios.

To use this feature, simply enter the email address of the user you wish to invite to the session. If the user is not registered, they will be prompted to log in.

Note The email function leverages the default email set by your browser and operating system. For instance, on Windows, you need to have your email account connected to the Email App for this functionality to work correctly.
Clone Packets
This is an advance feature for those that want the packet data they send up to the API. Click to get a JSON of the packet info sent to API This data contains the raw data we send to the API for processing. Most users can ignore this feature.

See prompt structure for more
Threshold Dialog
The Threshold Dialog is located within the Document Option and is designed to offer you a comprehensive view of your token count and give you better control over your interaction with the AI. The panel provides a summary of your session:

-
Max Tokenthe maximum alloted token for a specific model.
-
New Prompttoken count of the current input in the text area, has yet to be submitted.
-
System Messagetoken used in the system message.
-
Prompt Countprompts as a ratio between selected and unselected responses
-
Request SizeThis reflects the current token count in the context history (i.e., selected prompts), plus the value set for max tokens (the amount you set for the response back).
-
Model Limit:This indicates the token limit for the selected model.
Owner Tab
As an owner, you have additional tools at your disposal.

Add Labels: This is one of the places that allow you to add custom labels to your session, which aids in the organization and filtering of your documents.

Owner's Note: A space for you to write notes related to the session. These can be reminders, observations, or any information pertinent to the session.
Usage limits per session
Gives you a detailed report on token usage for the session, helping you to monitor and manage your resource usage more effectively.

Related See your total usage stats in profile settings below.
Profile Setting
The Profile Options is accessible from anywhere on the app and lets you personalize your user experience on Unacog. It's structured into three tabs: User, Labels, and Account.

User
Use this tab to personalize your profile image and personalize your experience

Name: Use the pencil icon to manually change your name, or the dice icon to generate a random one.

Profile Image: Upload a custom image or choose to generate a random mascot image.
Use the checkboxes to customize display settings and other preferences

Large Text: Check this box to increase the size of the chat interface text.
Monospace Font: Switch the font family to monospace for chat prompts and responses.
Auto Exclude: This feature automatically excludes the oldest prompt in your chat session to avoid going over the API token limit for each ChatGPT model. This option is also available on a session basis inside document options > threshold
KaTex: KaTeX is a JavaScript library for formatting math expressions on the web. If math formulas do not come out looking right, make sure you have Katex and Katex Inline checked.

KaTex Inline Sometimes the formatter can get tripped up by different notations, like the dollar sing "$". This feature is particularly useful when you need to include mathematical symbols or equations within paragraphs, headings, or any other text elements.
Labels
This section presents default labels (Personal, Business, and Archived) that you can assign to sessions during creation or afterwards. You can modify these labels according to your needs for better organization and filtering of your documents.

Account
This tab provides critical information about your usage.
Token Usage History: Provides a detailed breakdown of token usage by day, month, year, and all time based on sent messages and replies from the AI.

Monthly OpenAI Token Usage:
Displays the total token limit and your usage for the month.

New Email:
Allows you to migrate your document data to another email account.


